그리드 서치하는 이유: 최적의 파라미터 찾으려고.
찾고나면 그리드 서치 지워버리고 파라미터만 적용하기
ml13_gridSearchCV_iris
RandomForestClassifier()
param = [
{'n_estimators': [100,200], 'max_depth' : [6,8,10],
'n_jobs':[-1,1,2]},
{'n_estimators': [100,500], 'min_samples_leaf':[3,5,7]}
]
#2. 모델
rf_model = RandomForestClassifier()
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
model = GridSearchCV(rf_model, param, cv=kfold, verbose=1)선생님이 임의로 설정한 수치의 파라미터.
그리드서치하면 이 중에 최적의 값을 찾아서 출력해줌
Iris에 아래 파라미터 적용 후 돌
parameters = [
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200], 'max_depth':[6, 8, 10, 12], 'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]},
{'max_depth' : [6, 8, 10, 12], 'min_samples_split' : [2, 3, 5, 10]},
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200], 'min_samples_leaf' : [3, 5, 7, 10]},
{'min_samples_split' : [2, 3, 5, 10], 'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]},
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200],'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]}다른 파라미터랑 모델 수정
최적의 파라미터, 매개변수 찾기
전
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, cross_val_predict
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(77) # weight 난수값 조정
#1. 데이터
datasets = load_iris()
x = datasets['data']
y = datasets.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
x, y, train_size=0.8, shuffle=True, random_state=42
)
# kfold
n_splits = 5
random_state = 42
kfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=n_splits, shuffle=True,
random_state=random_state)
# Scaler 적용
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaler.fit(x_train)
x_train = scaler.transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
param = [
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200], 'max_depth':[6, 8, 10, 12], 'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]},
{'max_depth' : [6, 8, 10, 12], 'min_samples_split' : [2, 3, 5, 10]},
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200], 'min_samples_leaf' : [3, 5, 7, 10]},
{'min_samples_split' : [2, 3, 5, 10], 'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]},
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200],'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]}
]
#2. 모델
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
rf_model = RandomForestClassifier()
model = GridSearchCV(rf_model, param, cv=kfold, verbose=1,
refit=True, n_jobs=-1) #refit 기본값은 False라 꼭 True로 해줘야함: 위에 입력한 파라미터를 찾아서 적용하는 기능
#3. 훈련
import time
start_time = time.time()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
end_time= time.time() - start_time
print('최적의 파라미터 : ' , model.best_params_)
print('최적의 매개변수 : ' , model.best_estimator_)
print('best_score : ', model.best_score_)
print('model_score : ', model.score(x_test, y_test))
print('걸린 시간 : ', end_time, '초')결과 값
최적의 파라미터 : {'min_samples_leaf': 10, 'n_estimators': 200}
최적의 매개변수 : RandomForestClassifier(min_samples_leaf=10, n_estimators=200)
best_score : 0.9583333333333334
model_score : 1.0
걸린 시간 : 10.046573162078857 초결과 값 적용하는 코드 참고(최초 파라미터가 달라서 값이 다름 ㅜ )
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, cross_val_predict
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(77) # weight 난수값 조정
#1. 데이터
datasets = load_iris()
x = datasets['data']
y = datasets.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
x, y, train_size=0.8, shuffle=True, random_state=42
)
# kfold
n_splits = 5
random_state = 42
kfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=n_splits, shuffle=True,
random_state=random_state)
# Scaler 적용
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaler.fit(x_train)
x_train = scaler.transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
#2. 모델
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
model = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=6, n_estimators= 200, n_jobs= -1)
#refit 기본값은 False라 꼭 True로 해줘야함: 위에 입력한 파라미터를 찾아서 적용하는 기능
#3. 훈련
import time
start_time = time.time()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
end_time= time.time() - start_time
print('걸린 시간 : ', end_time, '초')
# 최적의 파라미터 : {'max_depth': 6, 'n_estimators': 200, 'n_jobs': -1}
# 최적의 매개변수 : RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=6, n_estimators=200, n_jobs=-1)
# best_score : 0.95
# model_score : 1.0
# 그리드 서치 후
# 걸린 시간 : 0.2216627597808838 초
# cv pred acc : 0.9666666666666667
#4. 평가, 예측
score = cross_val_score(model,
x_train, y_train,
cv=kfold) # cv : cross validation
# print('cv acc : ', score)
y_predict = cross_val_predict(model,
x_test, y_test,
cv=kfold)
# print('cv pred : ', y_predict)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
print('cv pred acc : ', acc)
# 결과
# SVC() 결과 acc : 0.9777777777777777
# MinMaxScaler : 0.9777777777777777
# ==================================
# tree 결과 acc : 0.9555555555555556
# ==================================
# ensemble 결과 acc : 0.9555555555555556
# kfold 결과 acc : 1.0ml13_gridSearchCV_california :
RandomForestRegressor, 그리드 돌리기
import numpy as np
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, StratifiedKFold, KFold
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, cross_val_predict
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import tensorflow as tf
tf.random.set_seed(77) # weight 난수값 조정
#1. 데이터
datasets = fetch_california_housing()
x = datasets['data']
y = datasets.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
x, y, train_size=0.8, shuffle=True, random_state=42
)
# kfold
n_splits = 5
random_state = 42
kfold = KFold(n_splits=n_splits, shuffle=True,
random_state=random_state)
# Scaler 적용
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
scaler.fit(x_train)
x_train = scaler.transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
param = [
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200], 'max_depth':[6, 8, 10, 12], 'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]},
{'max_depth' : [6, 8, 10, 12], 'min_samples_split' : [2, 3, 5, 10]},
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200], 'min_samples_leaf' : [3, 5, 7, 10]},
{'min_samples_split' : [2, 3, 5, 10], 'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]},
{'n_estimators' : [100, 200],'n_jobs' : [-1, 2, 4]}
]
#2. 모델
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
rf_model = RandomForestRegressor()
model = GridSearchCV(rf_model, param, cv=kfold, verbose=1,
refit=True, n_jobs=-1) #refit 기본값은 False라 꼭 True로 해줘야함: 위에 입력한 파라미터를 찾아서 적용하는 기능
#3. 훈련
import time
start_time = time.time()
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
end_time= time.time() - start_time
print('최적의 파라미터 : ' , model.best_params_)
print('최적의 매개변수 : ' , model.best_estimator_)
print('best_score : ', model.best_score_)
print('model_score : ', model.score(x_test, y_test))
print('걸린 시간 : ', end_time, '초')
#4. 평가, 예측
score = cross_val_score(model,
x_train, y_train,
cv=kfold) # cv : cross validation
# print('cv acc : ', score)
y_predict = cross_val_predict(model,
x_test, y_test,
cv=kfold)
# print('cv pred : ', y_predict)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
print('cv pred acc : ', acc)그리드 결과
최적의 파라미터 : {'n_estimators': 200, 'n_jobs': 4}
최적의 매개변수 : RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=200, n_jobs=4)
best_score : 0.8057484561327181
model_score : 0.8088843983852754
걸린 시간 : 466.20924973487854 초너무 오래걸려서 랜덤그리드서치로 가야함 ,, ,!!!
랜덤서치코드
#2. 모델
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV
rf_model = RandomForestRegressor()
model = RandomizedSearchCV(rf_model, param, cv=kfold, verbose=1,
refit=True, n_jobs=-1)
#refit 기본값은 False라 꼭 True로 해줘야함: 위에 입력한 파라미터를 찾아서 적용하는 기능랜덤서치값
최적의 파라미터 : {'n_estimators': 200, 'n_jobs': -1}
최적의 매개변수 : RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=200, n_jobs=-1)
best_score : 0.8057475283936508
model_score : 0.8070839473608384
걸린 시간 : 698.0324904918671 초xgboost 모델의 parameters
ml15_gridSearchCV_xgb_iris - Jupyter Notebook
그리드 적용 result : ml15_gridSearchCV_xgb_iris_result - Jupyter Notebook
LGBM 모델의 parameters -실습 안 했지만 팀플에 쓰기
catboost 모델의 parameters-실습 안 했지만 팀플에 쓰기
ml16_gridSearchCV_cat_iris - Jupyter Notebook
ml16_bagging_iris
원래 결과값이 좋은 데이터.
bagging : 성능 좋음
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import time
#1. 데이터
datasets = load_iris()
x = datasets.data
y = datasets.target
x_train,x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,train_size=0.8, random_state=42, shuffle=True)
# 스케일러
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
#2. 모델(Bagging)
bagging = BaggingClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(),
n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=-1,
random_state=42)
#3. 훈련
start_time = time.time()
bagging.fit(x_train,y_train)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
#4. 평가,예측
result = bagging.score(x_test,y_test)
print('걸린시간: ', end_time, '초')
print('bagging 결과 : ', result)
걸린시간: 1.556366205215454 초
bagging 결과 : 1.0ml16_bagging_cali
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
import time
#1. 데이터
datasets = fetch_california_housing()
x = datasets.data
y = datasets.target
x_train,x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,train_size=0.8, random_state=42, shuffle=True)
# 스케일러
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
#2. 모델(Bagging)
bagging = BaggingRegressor(DecisionTreeRegressor(),
n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=-1,
random_state=42)
#3. 훈련
start_time = time.time()
bagging.fit(x_train,y_train)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
#4. 평가,예측
result = bagging.score(x_test,y_test)
print('걸린시간: ', end_time, '초')
print('bagging 결과 : ', result)
# 걸린시간: 3.731471300125122 초
# bagging 결과 : 0.8042348744721923배깅 + kfold, grid
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingRegressor
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
import time
#1. 데이터
datasets = fetch_california_housing()
x = datasets.data
y = datasets.target
x_train,x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,train_size=0.8, random_state=42, shuffle=True)
# 스케일러
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
#KFold
n_split = 5
kfold = KFold(n_splits=n_split, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
#parameter
param ={
'n_estimators': [100],
'random_state':[42,62,72],
'max_features':[3,4,7]
}
#2. 모델(Bagging)
bagging = BaggingRegressor(DecisionTreeRegressor(),
n_estimators=100,
n_jobs=-1,
random_state=42)
model = GridSearchCV(bagging, param, cv=kfold, refit=True, n_jobs=-1)
#3. 훈련
start_time = time.time()
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
end_time = time.time() - start_time
#4. 평가,예측
result = model.score(x_test,y_test)
print('최적의 매개변수 : ', model.best_estimator_)
print('최적의 파라미터 : ', model.best_params_)
print('걸린시간: ', end_time, '초')
print('bagging 결과 : ', result)
#배깅만 했을 때
# 걸린시간: 3.731471300125122 초
# bagging 결과 : 0.8042348744721923
#kfold, grid 적용결과
# 최적의 매개변수 : BaggingRegressor(estimator=DecisionTreeRegressor(), max_features=7,
# n_estimators=100, n_jobs=-1, random_state=42)
# 최적의 파라미터 : {'max_features': 7, 'n_estimators': 100, 'random_state': 42}
# 걸린시간: 49.88687562942505 초
# bagging 결과 : 0.822087951242456파라미터 & 배깅 & kfold, grid 모두 넣으면 값이 더 좋아짐 !
voting : boost 여러 개의 다른 모델을 조합하여 더 강력하고 정확한 예측 모델을 만드는 방법
hard와 soft 차이 있음
iris voting classifier
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
from catboost import CatBoostClassifier
#1. 데이터
datasets = load_iris()
x = datasets.data
y = datasets.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.2, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
# 스케일러
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
#2. 모델(voting)
xgb = XGBClassifier()
lgbm = LGBMClassifier()
cat = CatBoostClassifier()
model = VotingClassifier(estimators=[('xgb', xgb),('lgbm', lgbm),('cat', cat)],# 모델이랑 이름 같이 넣어줘야함
voting = 'hard',
n_jobs=-1)
#3. 훈련
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
# 4. 평가 예측
# y_predict = model.predict(x_test)
# score = accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
# print('voting 결과: ', score)
classifiers = [cat,xgb,lgbm,]
for model in classifiers:
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
y_predict=model.predict(x_test)
score = accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
class_name = model.__class__.__name__
print('{0} 정확도: {1: .4f}'.format(class_name, score))
# CatBoostClassifier 정확도: 1.0000
# XGBClassifier 정확도: 1.0000
# LGBMClassifier 정확도: 1.0000california voting regressor
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
from catboost import CatBoostRegressor
#1. 데이터
datasets = fetch_california_housing()
x = datasets.data
y = datasets.target
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.2, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
# 스케일러
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
#2. 모델(voting)-모델에 그리드서치한 값을 각 클래스에 추가해서 돌리기
xgb = XGBRegressor()
lgbm = LGBMRegressor()
cat = CatBoostRegressor()
model = VotingRegressor(estimators=[('xgb', xgb),('lgbm', lgbm),('cat', cat)], # 모델이랑 이름 같이 넣어줘야함
n_jobs=-1) #regressor에선 괄호안에 voting 없음 , 하드 소프트는: 분류 모델에서만 사용.
#3. 훈련
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
# 4. 평가 예측
# y_predict = model.predict(x_test)
# score = accuracy_score(y_test, y_predict)
# print('voting 결과: ', score)
regressors = [cat,xgb,lgbm,]
for model in regressors:
model.fit(x_train,y_train)
y_predict=model.predict(x_test)
score = r2_score(y_test, y_predict)
class_name = model.__class__.__name__
print('{0} 정확도: {1: .4f}'.format(class_name, score))
#회귀는 hard soft 구분이 없음
# CatBoostRegressor 정확도: 0.8492
# XGBRegressor 정확도: 0.8287
# LGBMRegressor 정확도: 0.8365아웃라이어 - iqr 중심으로 보기, 손코딩, 시각화
import numpy as np
oliers = np.array([-50,-10,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,50])
def outliers (data_out):
quartile_1, q2, quartile_3 = np.percentile(data_out,
[25,50,75]) #등분하는거
print('1사분위 : ', quartile_1)
print('2사분위 : ', q2)
print('3사분위 : ', quartile_3)
iqr = quartile_3 - quartile_1
print('IQR : ',iqr)
lower_bound = quartile_1 - (iqr*1.5) #낮은 이상치
upper_bound = quartile_3 + (iqr*1.5) #높은 이상치
print('lower_bound : ', lower_bound)
print('upper_bound : ', upper_bound)
return np.where((data_out>upper_bound) |
(data_out<lower_bound))
outliers_loc = outliers(oliers)
print('이상치의 위치 : ', outliers_loc)
***********
1사분위 : 3.25
2사분위 : 6.5
3사분위 : 9.75
IQR : 6.5
lower_bound : -6.5
upper_bound : 19.5
이상치의 위치 : (array([ 0, 1, 13], dtype=int64),)컬럼별로 넣어서 이상치 확인 후 제거할 부분 제거 ;
#시각화
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.boxplot(oliers)
plt.show()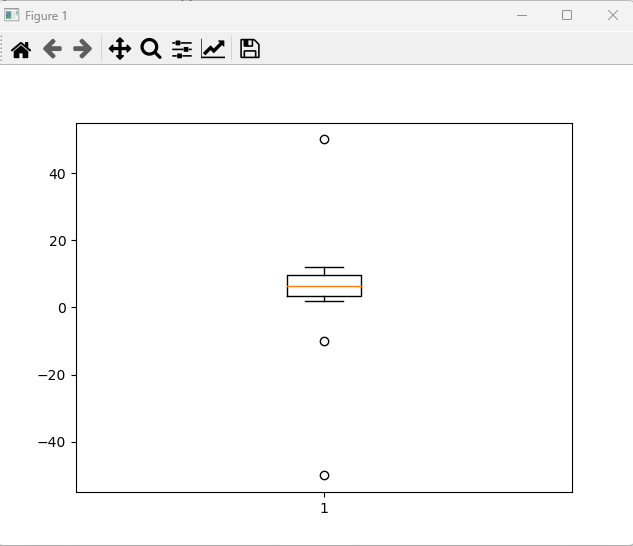
=> iqr 벗어나는 부분 삭제해도 됨 ;
ml18_outliers.EllipticEnvelope.py
import numpy as np
oliers = np.array([-50,-10,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,50])
print(oliers.shape) #(14,)
oliers = oliers.reshape(-1,1)
print(oliers.shape) #(14, 1)
from sklearn.covariance import EllipticEnvelope
outliers = EllipticEnvelope(contamination =.1) #이상치 몇 퍼 지정할지 정하기
outliers.fit(oliers)
result = outliers.predict(oliers)
print(result)
print(result.shape) #(14,)
#[-1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 -1]v결측치 확인
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = pd.DataFrame([[2, np.nan, 6,8,10],
[2,4,np.nan, 8,np.nan,],
[2,4,6,8,10],
[np.nan,4, np.nan, 8, np.nan]])
# print(data)
# print(data.shape)
# 0 1 2 3 4
# 0 2.0 NaN 6.0 8 10.0
# 1 2.0 4.0 NaN 8 NaN
# 2 2.0 4.0 6.0 8 10.0
# 3 NaN 4.0 NaN 8 NaN
# (4, 5)
data = data.transpose()
data.columns = ['x1','x2','x3', 'x4']
# print(data)
# print(data.shape)
# x1 x2 x3 x4
# 0 2.0 2.0 2.0 NaN
# 1 NaN 4.0 4.0 4.0
# 2 6.0 NaN 6.0 NaN
# 3 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0
# 4 10.0 NaN 10.0 NaN
# (5, 4)
#결측치 확인
print(data.isnull())
print(data.isnull().sum())
print(data.info())
# 1. 결측치 삭제
print(data.dropna(axis=0)) #난 값이 들어있는 컬럼이 다 없어짐
print(data.shape)
'''
# print(data.dropna())
# x1 x2 x3 x4
# 3 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0
# (5, 4)
# axis=0이면 컬럼 다 살아있는데 행이 사라짐
x1 x2 x3 x4
3 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0
(5, 4)
# axis=1이면 컬럼 열이 다 사라짐
x3
0 2.0
1 4.0
2 6.0
3 8.0
4 10.0
(5, 4)
'''
'''
#2. 특정값으로 대체
means = data.mean() # 평균
median = data.median() #중간 값
data2 = data.fillna(means)
print(data2)
x1 x2 x3 x4
0 2.0 2.000000 2.0 6.0
1 6.5 4.000000 4.0 4.0
2 6.0 4.666667 6.0 6.0
3 8.0 8.000000 8.0 8.0
4 10.0 4.666667 10.0 6.0
data3= data.fillna(median)
print(data3)
x1 x2 x3 x4
0 2.0 2.0 2.0 6.0
1 7.0 4.0 4.0 4.0
2 6.0 4.0 6.0 6.0
3 8.0 8.0 8.0 8.0
4 10.0 4.0 10.0 6.0
'''sklearn으로 결측지 값 정리
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
data = pd.DataFrame([[2, np.nan, 6,8,10],
[2,4,np.nan, 8,np.nan,],
[2,4,6,8,10],
[np.nan,4, np.nan, 8, np.nan]])
data = data.transpose()
data.columns = ['x1','x2','x3', 'x4']
# from sklearn.impute import IterativeImputer
# from sklearn.experimental import enable_iterative_imputer
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
# imputer = SimpleImputer() #평균값으로 대체(default)
# imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='mean') #평균값
# imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='median') # 중간값
# imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent') #가장 많이 사용된 값
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='constant', fill_value=777) #상수 입력값, default = 0
imputer.fit(data)
data2 = imputer.transform(data)
print(data2)
'''
imputer = SimpleImputer()
[[ 2. 2. 2. 6. ]
[ 6.5 4. 4. 4. ]
[ 6. 4.66666667 6. 6. ]
[ 8. 8. 8. 8. ]
[10. 4.66666667 10. 6. ]]
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='median') # 중간값
[[ 2. 2. 2. 6.]
[ 7. 4. 4. 4.]
[ 6. 4. 6. 6.]
[ 8. 8. 8. 8.]
[10. 4. 10. 6.]]
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='most_frequent')
[[ 2. 2. 2. 4.]
[ 2. 4. 4. 4.]
[ 6. 2. 6. 4.]
[ 8. 8. 8. 8.]
[10. 2. 10. 4.]]
imputer = SimpleImputer(strategy='constant', fill_value=777)
[[ 2. 2. 2. 777.]
[777. 4. 4. 4.]
[ 6. 777. 6. 777.]
[ 8. 8. 8. 8.]
[ 10. 777. 10. 777.]]
'''데이터 확인 후 숫자 너무 큰건 줄여주기
#log 변환
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score, cross_val_predict
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler, StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import MaxAbsScaler, RobustScaler
#1. 데이터
datasets = fetch_california_housing()
x = datasets['data']
y = datasets.target
df = pd.DataFrame(x, columns=[datasets.feature_names])
print(df)
print(df.head())
print(df['Population']) #다른데이터에 비해 숫자가 너무 큼 다른건 다 2자리 이하인데 이건 4자리
df['Population'] = np.log1p(df['Population'])
print(df['Population'].head())
Population
0 5.777652
1 7.784057
2 6.208590
3 6.326149
4 6.338594'[네이버클라우드] 클라우드 기반의 개발자 과정 7기 > AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 머신러닝 2 /GridSearch, outlier, Bagging, Voting (0) | 2023.05.16 |
|---|---|
| [수업자료] ml1 오늘의 코드3 (0) | 2023.05.16 |
| 머신러닝 1 / feature importance (0) | 2023.05.16 |
| 머신러닝 1 -model, scaling (0) | 2023.05.15 |
| heatmap NaN, label Encoding - 팀플 쓰기 (2) | 2023.05.12 |